Fishing Operations
State of the art fishing for last decade, we operate fishing fleet in Omani waters. We built coastal fishing boats, chartered fishing boats and contracted local Artishana boats for the industry in order to supply quality and quantity fish to local and interstate for our seafood customers.
In addition, we offer fishing consultation to all type of ship owners with licensing cooperation for longliner, trawler,gill-netter,purse seiner in the Indian Ocean. Our professional team brings years of experience in the field and is always on call. Having partnership with professional fishery consultancy firm expands fishing licensing up to Atlantic Ocean and Pacific Ocean countries. Welcome interested customers to have business talk with us !
In addition, we offer fishing consultation to all type of ship owners with licensing cooperation for longliner, trawler,gill-netter,purse seiner in the Indian Ocean. Our professional team brings years of experience in the field and is always on call. Having partnership with professional fishery consultancy firm expands fishing licensing up to Atlantic Ocean and Pacific Ocean countries. Welcome interested customers to have business talk with us !
Longline Fishing
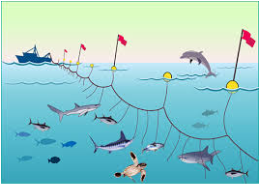
Method
Longlines can be used to capture fish in surface waters (pelagic) as well as bottom living species (demersal). Longlining sets a length of line and from this come branch lines carrying baited hooks. Large longlines used offshore can be tens of kilometres long and carry thousands of hooks. Smaller inshore vessels use shorter, lighter lines with roughly less than a thousand hooks.
Examples of target species
Pelagic such as Tuna,swordfish and demersal eg. halibut and cod, groupers ,etc.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – longlines do not drag along the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – longlines can unintentionally catch vulnerable species and high seas fisheries have been particularly associated with catching endangered seabirds, sharks and sea turtles.
Longlines can be used to capture fish in surface waters (pelagic) as well as bottom living species (demersal). Longlining sets a length of line and from this come branch lines carrying baited hooks. Large longlines used offshore can be tens of kilometres long and carry thousands of hooks. Smaller inshore vessels use shorter, lighter lines with roughly less than a thousand hooks.
Examples of target species
Pelagic such as Tuna,swordfish and demersal eg. halibut and cod, groupers ,etc.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – longlines do not drag along the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – longlines can unintentionally catch vulnerable species and high seas fisheries have been particularly associated with catching endangered seabirds, sharks and sea turtles.
Trawling Fishing
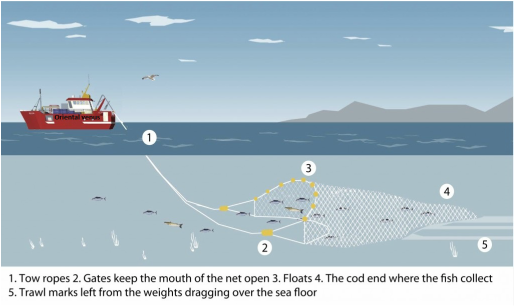
Method - Otter (single), twin-rig and pair trawlers:
In demersal trawl fisheries, a funnel-shaped net is towed behind either one (single trawl) or two (pair–trawl) boats. Once the net has been towed it is drawn out of the water to collect the captured fish. Twin-rig trawls follow the same principle but tow two nets. These demersal trawling methods fish along or just above the seafloor catching bottom dwelling fish.
Beam trawlers:
Beam trawls target fish on the seabed. They tow a net from either side of the boat. The mouth of the net is weighted and kept open by a metal beam that can be up to 12m long. Metal ‘tickler chains’ are attached to the gear to disturb fish from under the surface of the seabed and into the trawl.
Seine netting:
Seine netters use a net that is vertical in the water, with very long ropes attached leading back to the vessel. These drag on the ground, setting up a sand or mud cloud, which herds fish into the net.
Examples of target species
Otter and pair-trawls – cod, haddock, whiting and flatfish.
Twin-rig trawl – langoustine and prawns.
Beam trawl – flatfish, such as plaice and sole.
Seine netting – cod, haddock, whiting.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – damage and disturbance to the seabed and bottom living marine animals occurs as the fishing gear comes into contact with the ocean floor. Sensitive habitats, such as corals, are more susceptible to long-term damage than areas of sand and mud, which tend to be less severely impacted. The heavy gear dragged by beam trawlers is particularly notable in habitat damage.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – demersal trawls may unintentionally catch vulnerable species such as skates which, like trawl target species, are demersal.
In demersal trawl fisheries, a funnel-shaped net is towed behind either one (single trawl) or two (pair–trawl) boats. Once the net has been towed it is drawn out of the water to collect the captured fish. Twin-rig trawls follow the same principle but tow two nets. These demersal trawling methods fish along or just above the seafloor catching bottom dwelling fish.
Beam trawlers:
Beam trawls target fish on the seabed. They tow a net from either side of the boat. The mouth of the net is weighted and kept open by a metal beam that can be up to 12m long. Metal ‘tickler chains’ are attached to the gear to disturb fish from under the surface of the seabed and into the trawl.
Seine netting:
Seine netters use a net that is vertical in the water, with very long ropes attached leading back to the vessel. These drag on the ground, setting up a sand or mud cloud, which herds fish into the net.
Examples of target species
Otter and pair-trawls – cod, haddock, whiting and flatfish.
Twin-rig trawl – langoustine and prawns.
Beam trawl – flatfish, such as plaice and sole.
Seine netting – cod, haddock, whiting.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – damage and disturbance to the seabed and bottom living marine animals occurs as the fishing gear comes into contact with the ocean floor. Sensitive habitats, such as corals, are more susceptible to long-term damage than areas of sand and mud, which tend to be less severely impacted. The heavy gear dragged by beam trawlers is particularly notable in habitat damage.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – demersal trawls may unintentionally catch vulnerable species such as skates which, like trawl target species, are demersal.
Gill-net /Drifting Fishing
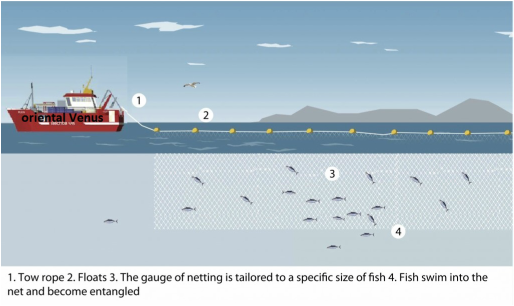
Method
Passive nets are not actively towed by boats; they are either placed to drift on the prevailing currents (drift netting), hung from buoys which keep them suspended between the surface and the seabed (gill nets), or staked to the seabed (set nets).
These nets hang like vertical walls in the water and capture fish by the gills as they try to swim through the mesh of the net.
Examples of target species
Gill netting – demersal species such as red snapper, Dover sole, mullet.
Drift netting – tuna, squid and shark.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – passive nets are not towed along the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – passive nets may unintentionally catch vulnerable species and have been particularly associated with catching dolphins, porpoises, sharks and other large marine life.
Passive nets are not actively towed by boats; they are either placed to drift on the prevailing currents (drift netting), hung from buoys which keep them suspended between the surface and the seabed (gill nets), or staked to the seabed (set nets).
These nets hang like vertical walls in the water and capture fish by the gills as they try to swim through the mesh of the net.
Examples of target species
Gill netting – demersal species such as red snapper, Dover sole, mullet.
Drift netting – tuna, squid and shark.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – passive nets are not towed along the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – passive nets may unintentionally catch vulnerable species and have been particularly associated with catching dolphins, porpoises, sharks and other large marine life.
Purse Seine Fishing
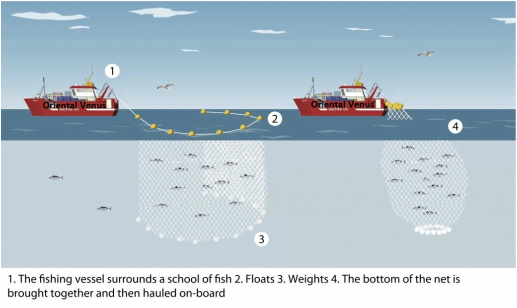
Method
Purse seines are large, vertically floating nets (made of monofilament or plastic) which boats use to surround shoals of fish they have identified on a fish finding sonar. Each net can be up to one mile long. Once fish are in the net, the base is drawn together, creating a ‘purse’. This method catches large volumes of fish. It is also used for catching live tuna for ongrowing in pens (called ‘ranching’).
Examples of target species
Tuna (both for direct capture and ranching), herring, mackerel.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – purse seines do not come into contact with the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – depending on the fishery, purses seines may catch vulnerable species; purse seining targeting tuna has been particularly associated with notable bycatch of mammals and sharks.
Purse seines are large, vertically floating nets (made of monofilament or plastic) which boats use to surround shoals of fish they have identified on a fish finding sonar. Each net can be up to one mile long. Once fish are in the net, the base is drawn together, creating a ‘purse’. This method catches large volumes of fish. It is also used for catching live tuna for ongrowing in pens (called ‘ranching’).
Examples of target species
Tuna (both for direct capture and ranching), herring, mackerel.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – purse seines do not come into contact with the seabed so are not associated with damage to marine habitat.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – depending on the fishery, purses seines may catch vulnerable species; purse seining targeting tuna has been particularly associated with notable bycatch of mammals and sharks.
Pots and creels (Trap)Fishing
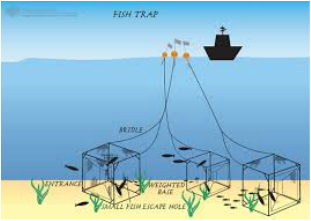
Method
Pots and creels are traps, baited with fresh or salted fish, which are laid on the seabed and primarily used to catch shellfish. Pots and creels are a selective method of fishing. Small individuals can escape the traps and the shellfish are brought aboard live so any unwanted catch can be return to the sea unharmed. Large vessels on long fishing trips will keep their shellfish in live holding tanks onboard, while small vessels tend to land their catch daily.
Examples of target species
Grouper,Crab, lobster, whelk, langoustines and octopus.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – pots and creels sit on the seabed so can be associated with disturbance to marine habitat but are not damaging.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – pots and creels are not particularly associated with unintentional capture of vulnerable species.
Pots and creels are traps, baited with fresh or salted fish, which are laid on the seabed and primarily used to catch shellfish. Pots and creels are a selective method of fishing. Small individuals can escape the traps and the shellfish are brought aboard live so any unwanted catch can be return to the sea unharmed. Large vessels on long fishing trips will keep their shellfish in live holding tanks onboard, while small vessels tend to land their catch daily.
Examples of target species
Grouper,Crab, lobster, whelk, langoustines and octopus.
Environmental summary
Habitat damage – pots and creels sit on the seabed so can be associated with disturbance to marine habitat but are not damaging.
Bycatch of vulnerable species – pots and creels are not particularly associated with unintentional capture of vulnerable species.

